Determining Your Unemployment Benefits
Unemployment benefits are administered by the U.S Labor Department under Federal Law. You should report all your unemployment benefits to the IRS.
In the US, there are 50 states that provide unemployment insurance programs. Along with that, there is the United States Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia.
Based on the eligibility and the benefits by state in 2023, it can be as high as $1282 per week in Massachusetts or as low as $5 per week in Hawaii.
Eligibility requirements differ by state but generally, employees not fired for misconduct are eligible for unemployment benefits.
Employees that quit without ‘good cause’ are not eligible for unemployment benefits. In some states, if you are fired you could be disqualified for a short period.
What is the Base Period?
The Base Period is defined as the period of employment before you lost your job. This is also known as the Base Year. Usually, the base period is the first four of the last five completed calendar quarters. This is before the effective date of unemployment.
A Calendar quarter is a quarter of a calendar year. Each quarter would comprise of three months and there are four quarters in each year. The following are the 4 calendar quarters:
- First Quarter: January, February, March
- Second Quarter: April, May, June
- Third Quarter: July, August, September
- Fourth Quarter: October, November, December
How To Consider the Base Period?
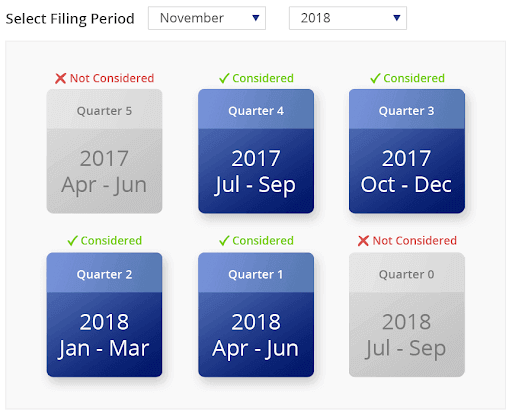
When it comes to Base Period if your unemployment claim is filed in November 2018. Then the base period is July 2017 through June 2018.
In order for the base period to be considered valid, the employment must be covered or insured. This means that the employer would have contributed unemployment insurance taxes to the government. Base period helps determine the monetary eligibility and what a person is entitled.
What happens if you have not worked for more than a year? You may qualify for the alternate base period. An alternate base period is the last four calendar quarters prior to unemployment. The alternate base period is not something you can choose to use.
It can be used only if you cannot establish monetary entitlement using your wages in the traditional base period. If you have not earned sufficient wages during your traditional base period. Then, the state government will apply the alternate base period to the claim to determine monetary eligibility.
Therefore, information proof is needed to determine the alternate base period. This includes the most recent quarter earning, proof of wages earned. Proof could be in the form of pay stubs and verification of wages earned during the quarter from your employer.
Tools to Determine the Unemployment Benefits
You can use these 3 tools to check your unemployment benefits:
Base Period Calculator: Find out your base period by selecting the month and year of the filing period. Moreover, unemployment benefits change based on the base period.
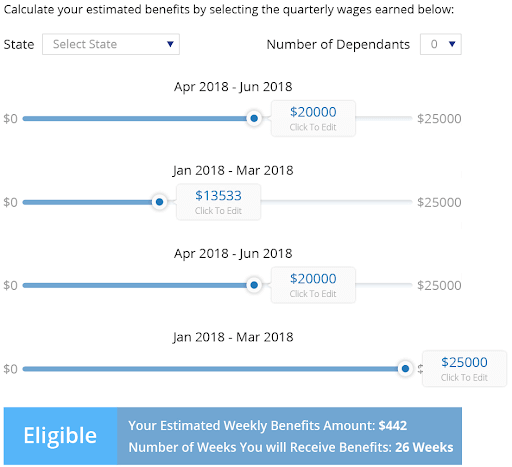
Unemployment Benefits Calculator: Using the Unemployment Benefits Calculator, you will know if you are eligible to receive benefits, the amount of weekly benefits and the number of weeks that you will receive benefits.
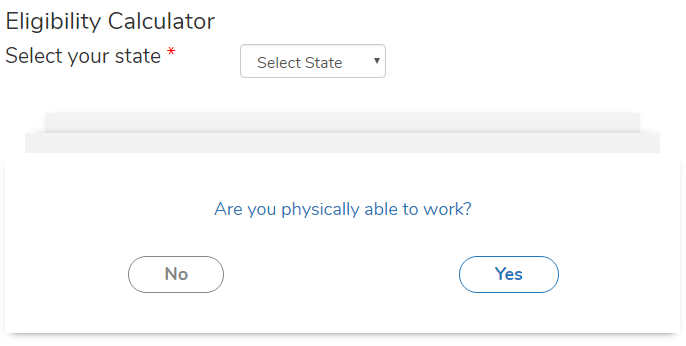
Eligibility Calculator: Find out if you are eligible for benefits. Just follow the steps and the Eligibility Calculator will let you know if you are eligible. However, this is important as you will know why you are eligible or not.
How To Calculate Benefits?
To calculate your weekly benefits amount, you should:
- Determine the base period for calculating unemployment.
- Review the base period when you received the highest pay.
- Calculate the highest quarter earnings using the Unemployment Benefits Calculator.
- Calculate what your weekly benefits would be if you have another job.
Be sure to calculate your unemployment benefits for every week if the partial gross income is different.